Research #11 Yatharth Hospital & Trauma Care Services Ltd
Welcome to the 11th edition of our small-cap coverage.
Welcome to the 11th edition of our small-cap coverage. Today, we're diving into a Hospitality business, ‘Yatharth Hospital & Trauma Care Services Ltd’
Let's start! But before we do, here is the link to the 10th edition.
We post a new edition every 2nd Saturday. So Subscribe and stay tuned for our upcoming publications on various companies.
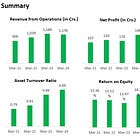
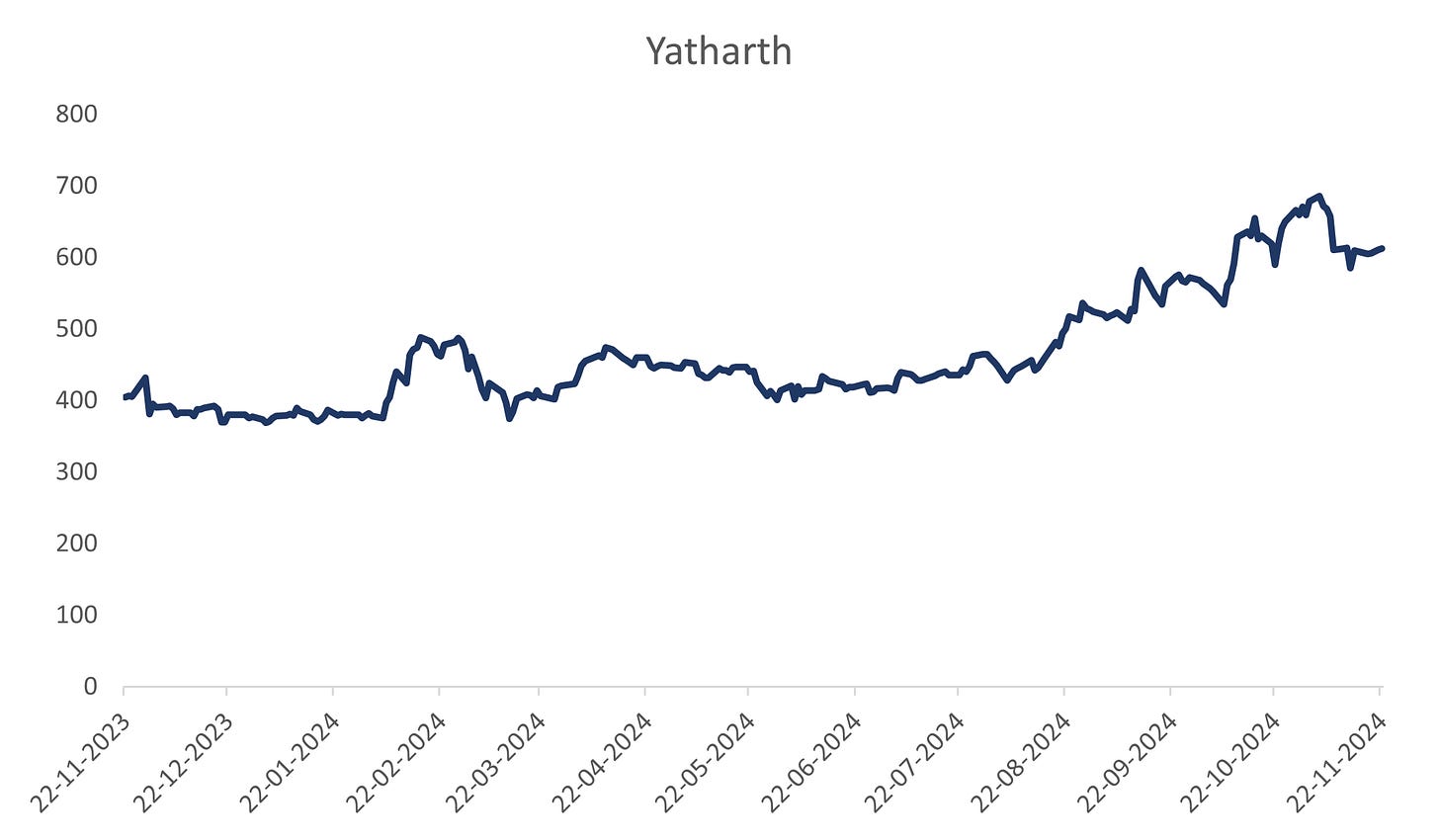
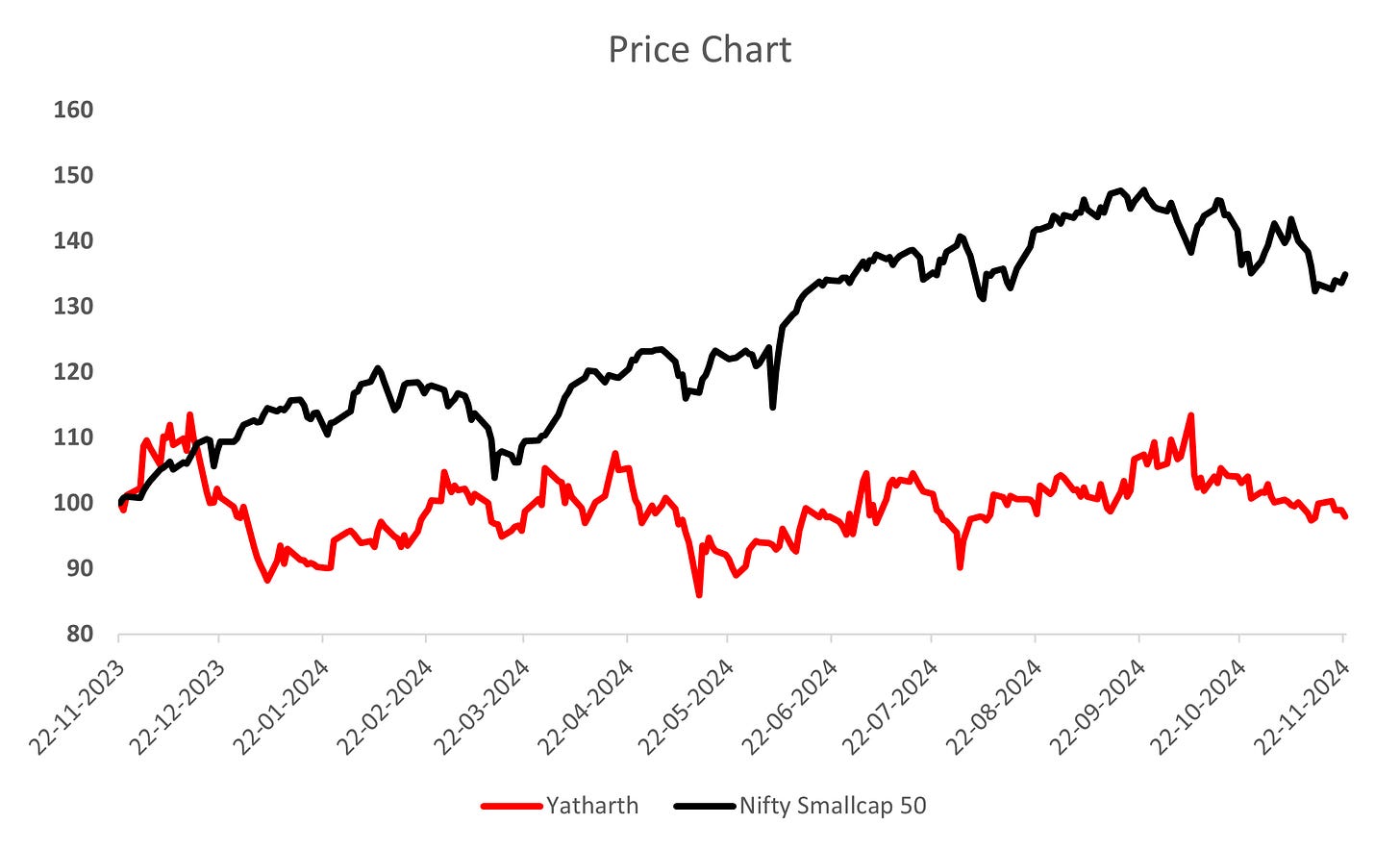
1. Company Share Price chart & comparison with Index:
All above charts are *Indexed on 22 November 2023 (=100)
2. About Company:
Yatharth Hospital is a multi-speciality healthcare provider in India, offering advanced treatments, trauma care, and critical services with a focus on affordability and quality.
Basic key points:
Registered Name:Yatharth Hospital & Trauma Care Services Limited.
Establishment: 2008.
Products: Multi-specialty treatments,Trauma and emergency care,Critical care services,Advanced diagnostics,Surgical services.
Industry: Healthcare & Hospitals
Listed on: Both NSE and BSE.
Website: https://www.yatharthhospitals.com/
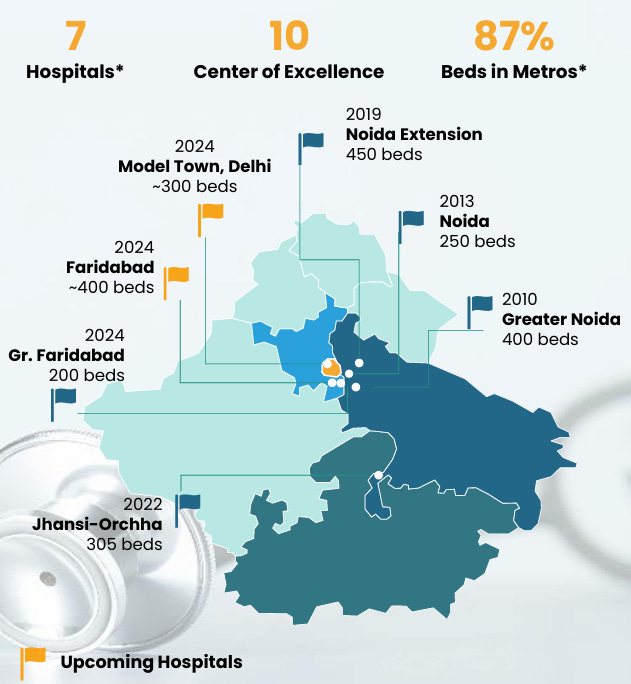
Location of Hospitals:
3. Company Journey
4. Managerial Overview:
5. Business Model of Yatharth
i). Revenue Model:
- Operates on a fee-for-service basis, generating income through consultations, treatments, and surgeries.
- Significant revenue stream from health insurance reimbursements.
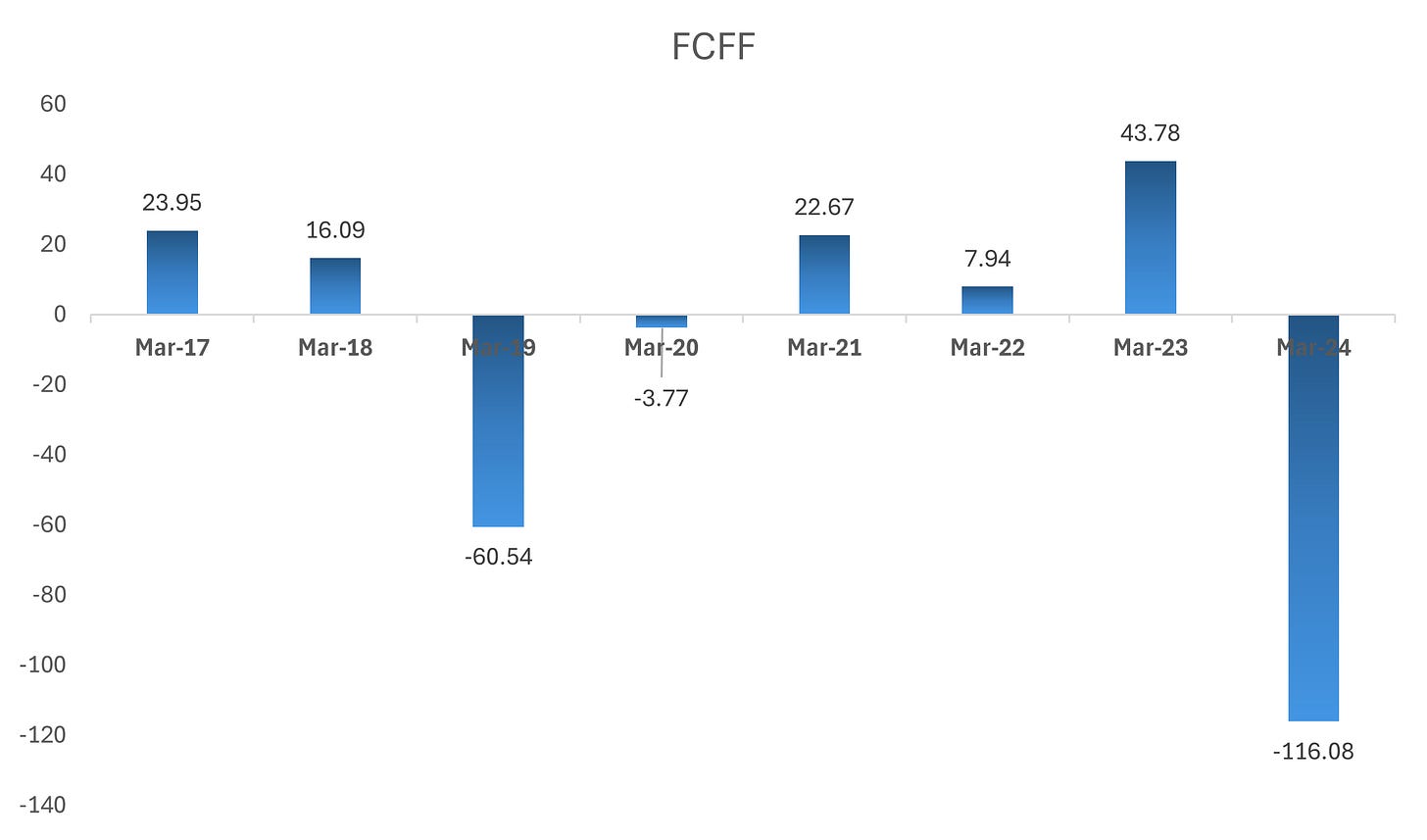
ii). Cash Flow Analysis
- Observation: The company exhibits fluctuating free cash flow (FCFF), reflecting periods of high capital investments. Notably, FCFF turned negative in FY23 due to significant outflows aimed at expansion.
- Implication: Despite some volatility, the company demonstrates the ability to generate positive cash flow in key years, supporting future scalability.
iii). Selling Strategies
- Maximizing Sales to Existing Customers:
Yatharth leverages advanced medical services and patient loyalty to increase revenue from existing clientele.
- Expanding Sales to New Customers:
Expansion into new geographic areas and catering to previously underserved markets drives patient volume growth.
- Introducing New Services to Existing Customers:
The introduction of high-margin services (e.g., advanced diagnostics, robotic surgeries) contributes to ARPOB growth.
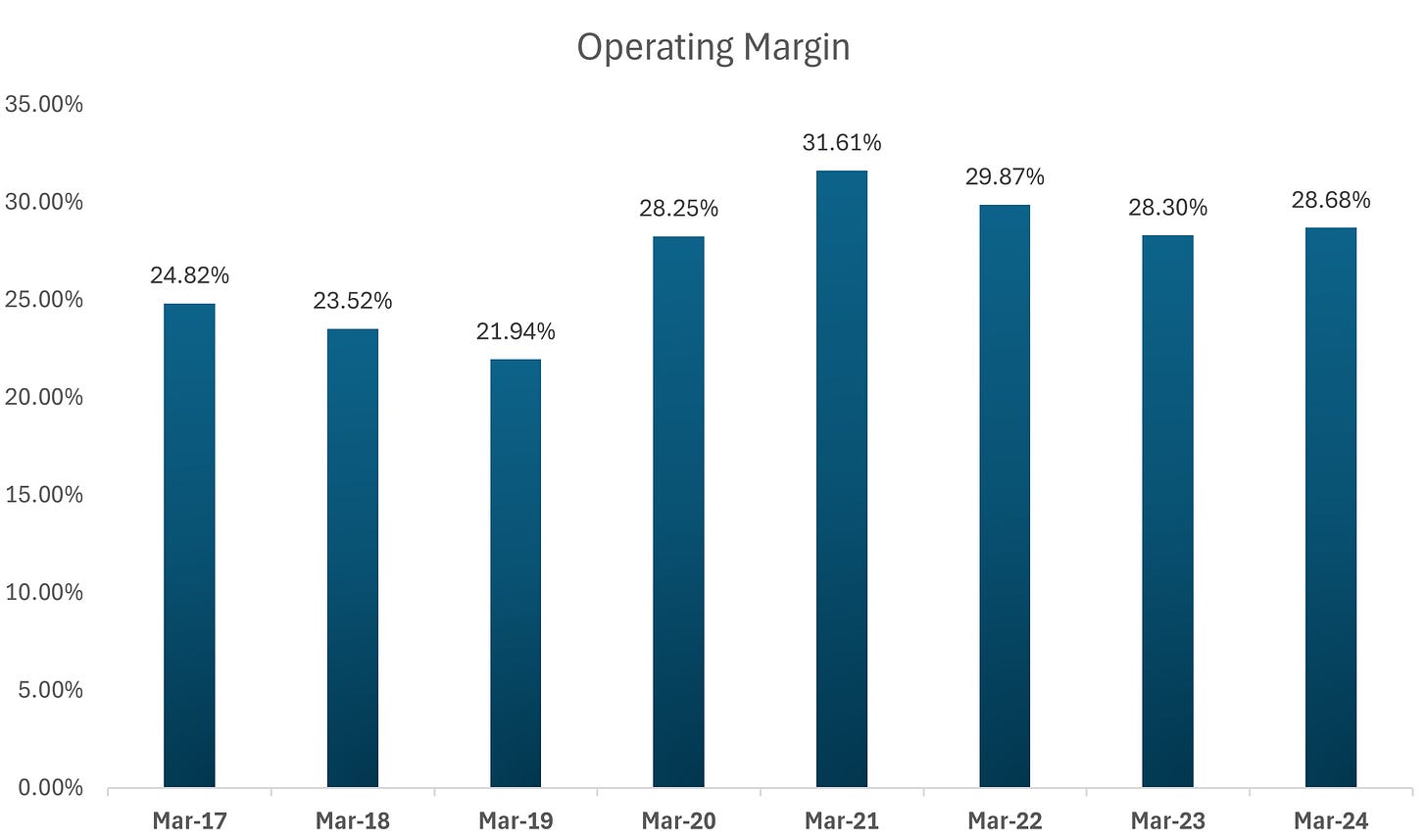
iv). Low-Cost Producer
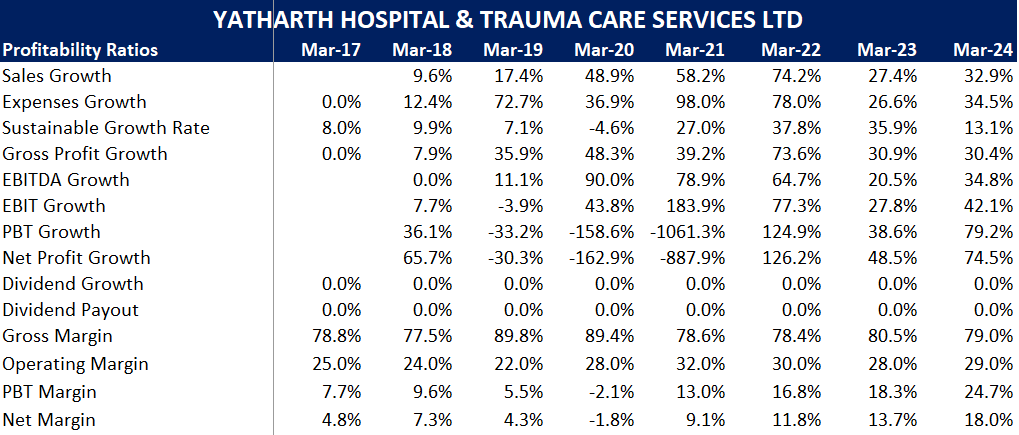
- Analysis: With operating margins averaging above 28% in recent years, Yatharth benefits from efficient cost structures, though employee costs slightly reduce its low-cost producer status.
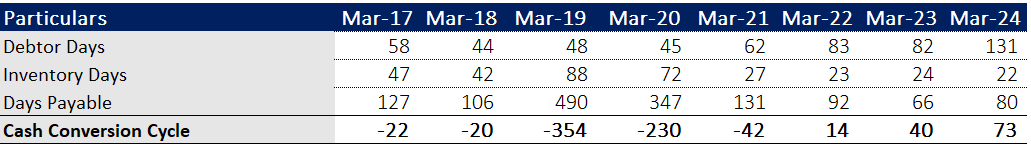
v). Working Capital Management
The Debtor Days and Inventory Days impact working capital efficiency. High debtor days (130.56 days) suggest that the company is not efficiently managing its receivables, tying up cash in outstanding payments.
Takeaway: The poor performance in receivables collection reduces the overall benefit to working capital. Improving debtor collection should be a focus.
vi). Entry Barriers
- Observation: Regulatory approvals, accreditation, high capital intensity, and brand reputation form strong entry barriers.
- Impact: These factors sustain the company's pricing power and competitive edge.
vii). Growth Analysis
- Volume Growth: The hospital network expansion aligns with growing population health needs and rising healthcare awareness.
- Pricing Power: The company’s ability to enhance ARPOB suggests strong pricing power backed by quality services.
viii). Re-investment of Cash Flow
- Observation: Significant capex indicates heavy reinvestment into infrastructure, technology, and new hospitals, reflecting a growth-oriented model.
ix). First Mover Advantage
- Observation: Expansion into underserved markets grants a partial first-mover advantage, particularly in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
x). Pricing Power
- Observation: Steady growth in ARPOB reflects strong pricing power without customer attrition.
xi). ROE (Return on Equity)
- Observation: The company’s ROE remains moderate, emphasizing the need for consistent margin improvement and operational scaling.
xii). Operational Efficiency
- Observation: Strong focus on cost containment and employee efficiency enhances margins, though a slight uptick in other manufacturing expenses warrants monitoring.
6. ESOPs:
The maximum number of options that may be granted in one or more tranches, under this Scheme will not exceed 2,50,000 (Two Lakh Fifty Thousand).
Options which shall be convertible into an equal number of Shares not exceeding 2,50,000 (Two Lakh Fifty Thousand) Equity Shares having a face value of Rs. 10/- each
If you like the hard work we put in, you can invest in us:
For our Non-Indian audience: You can donate to us through PayPal. Click here.
For our Indian audience, UPI QRs are given below:
7. Key Products/ Services:
Yatharth Hospital & Trauma Care Services Ltd provides a comprehensive range of healthcare services.
The hospital features Centres of Excellence specialising in:
Internal Medicine.
Neurosciences.
Oncology.
Nephrology & Urology.
Cardiology.
General Surgery.
Pulmonology.
Orthopaedics, Spine & Rheumatology.
Gastroenterology.
Gynaecology.
Paediatrics.
Additionally, the hospital offers a wide array of other speciality services.
8. Revenue/ Turnover Analysis:
9. Company’s Financial Analysis:
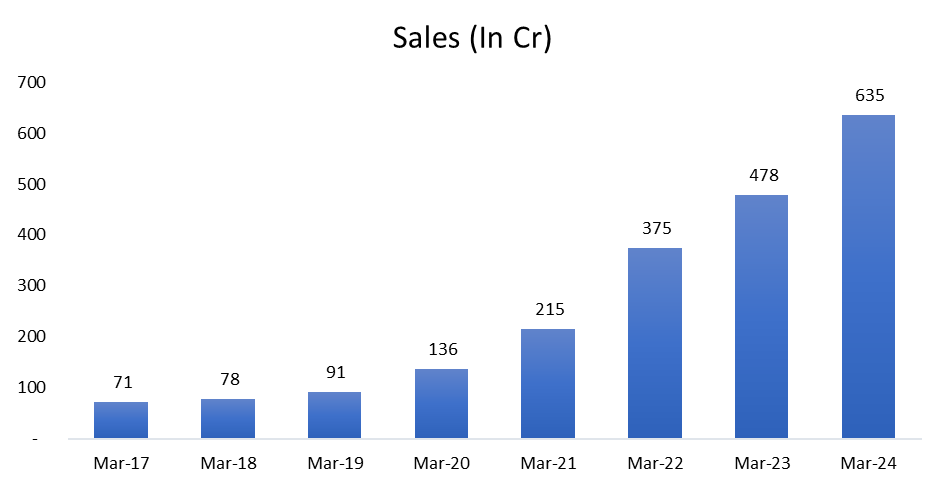
SALES
The Sales have grown at a CAGR of ~37% in the past 8 years.
Gross Profit Margin %
Gross profits have been increasing continuously at a CAGR of ~37% for the past 8 years.
The gross margins have come down to their pre COVID levels due to material costs again seeing an uptrend.
EBITDA Margin %
EBITDA has been increasing continuously at a CAGR of ~39% for the past 8 years.
EBITDA Margins have improved on the account of lower Employee costs and Other expenses.
Net Profit Margin %
Net profits have continuously increased at a CAGR of ~65% for the past 8 years.
Net profits decreased and became negative during FY25 due to a sudden rise in depreciation and interest expense for the company.
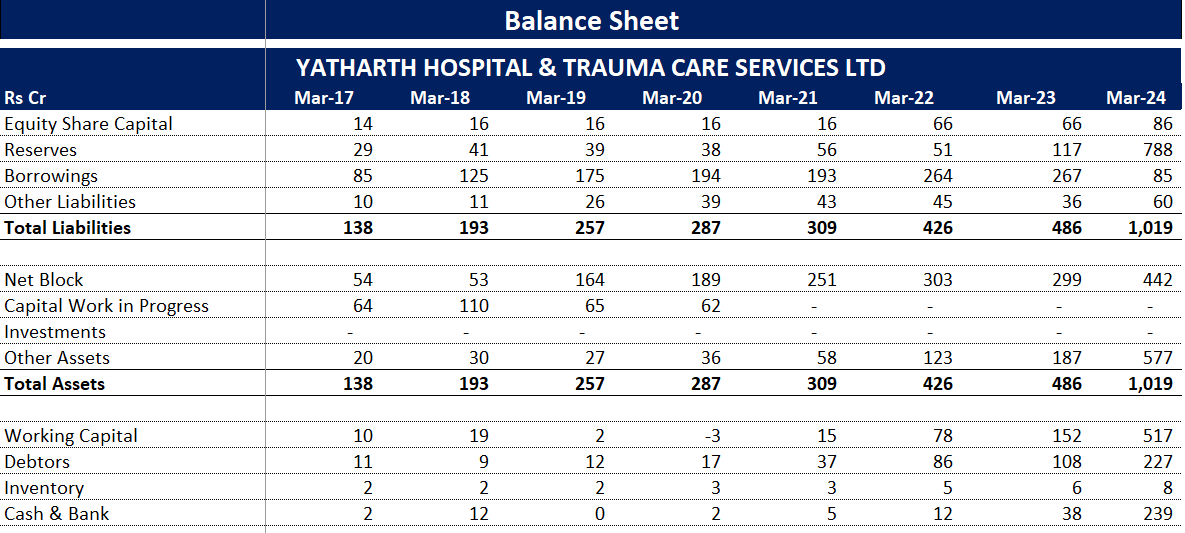
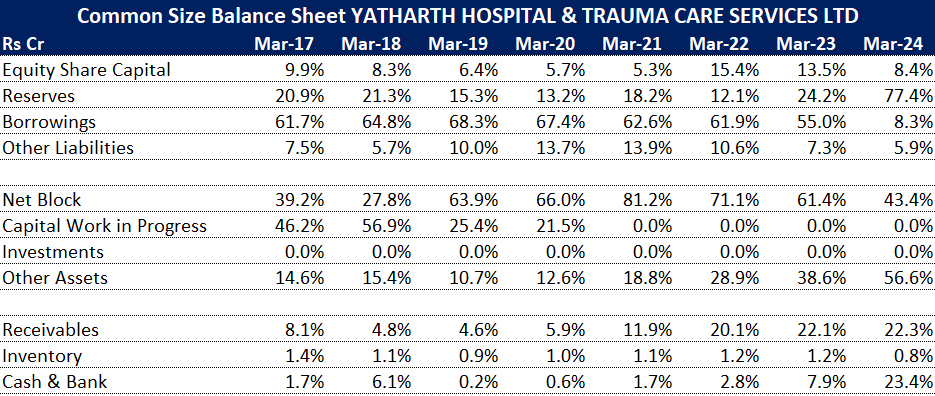
BALANCE SHEET:
Long-term borrowings have come down from FY24 after IPO proceeds from FY23 being used to pay off debt..
Fixed assets have increased significantly, pointing towards expansion.
Cash has increased on account of increased reserves from IPO proceeds.
Cash Receivables (% of Total Assets) has increased since FY22. Majority of it comes from the book of companies acquired through acquisition. . As per the management, by optimising the payer mix debtors have reduced and the working capital days at the end of September '24, have reduced to 104 days compared to 130 days in March '24 despite high growth in H1. The company is confident to bring down the days to 100 by the end of FY25.
Cashflow Statement:
The major drop in the CFO in FY24 is due to a dramatic increase in Trade Receivable
KEY RATIOS:
Cash Conversion Cycle:
Debtor days increased due to higher Receivables on account of acquisitions. As per the management it has come down to 105 days in Q2FY25.
The inventory days have decreased.
Payable days have decreased.
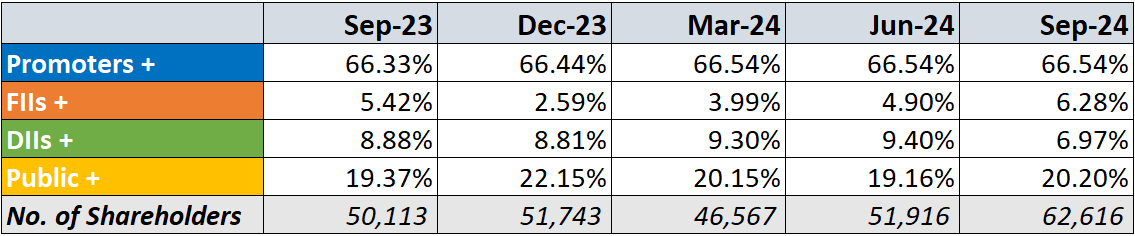
10. Shareholding Pattern:
FIIs have increased their holdings.
DIIs have decreased their holdings.
11. MD&A:
Indian Economy:
GDP:
Global GDP is projected to grow at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025. The trades have become firm supported by the strong exports from Asia, especially the technology sector. The businesses are majorly on ‘cost-cutting’ projects as the discretionary spendings are still low. Governments are facing fiscal challenges due to higher interest rates, spending on citizen schemes and climate change.
(Source: IMF, World Bank)
Inflation:
The economy has stayed remarkably resilient and thus, the inflation is coming back to the target level. Even during the high-inflationary environment, the consumption was still on rise especially in the emerging economies. The economy, despite facing deflation and recession warnings, has been growing steadily. Forecasts suggest for inflation to come down from 6.8% in 2023 to 5.9% in 2024 and 4.5% in 2025 globally.
(Source: IMF, World Bank)
Indian healthcare sector:
The healthcare sector is critical to India's journey toward becoming a developed economy.
Over the years, the sector has significantly transformed, contributing to:
Increased life expectancy.
Reduced maternal and child mortality rates.
Recognized as the "archetype of affordable healthcare", the domestic healthcare industry:
Plays a significant role in India's GDP.
Promotes public health both nationally and globally.
Financial and Investment Highlights:
FY 2024 budget allocation for healthcare: ₹89,155 crore (+13% from FY 2023).
Annual average growth rate of 12% from FY 2013 to FY 2024.
The hospital industry constitutes 80% of the total healthcare market.
Witnessed increased investments from domestic and global investors.
Growth drivers include India’s favorable business environment, mature pharmaceutical sector, and growing middle-class healthcare expenditure.
Technological Integration:
Digitalization and AI have enhanced:
Accurate disease diagnosis.
Improved treatment options.
Initiatives like the CoWIN App, Arogya Setu, and Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission have significantly benefited citizens across India.
12. Q2 FY25 Concall Analysis
Performance Highlights:
Revenue and Growth:
Revenue for Q2 FY25: ₹2,178 million, reflecting a 27% YoY growth and a 3% QoQ growth.
H1 FY25 revenue: ₹4,296 million, a growth of 32% YoY.
Revenue drivers include increased occupancy rates and Average Revenue Per Occupied Bed (ARPOB).
Profitability:
EBITDA: ₹546 million for Q2 FY25, up 20% YoY, but EBITDA margins slightly declined to 25.1% (from 26.6% in Q2 FY24) due to losses from the newly operational Greater Faridabad unit.
Net profit for Q2 FY25: ₹310 million, a 12% YoY increase.
Key Metrics:
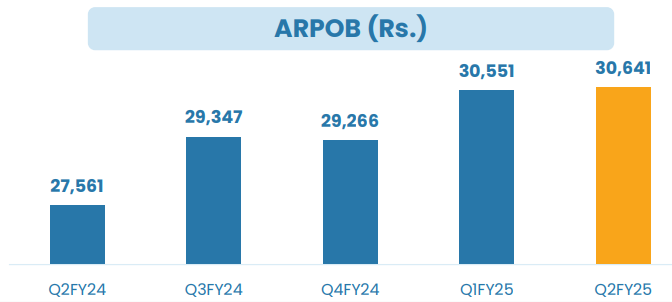
ARPOB: ₹30,641 for Q2 FY25, a 11% YoY increase.
Noida Extension ARPOB: ₹38,136, driven by high-value specialty services.
Occupancy: Group occupancy for H1 FY25 increased to 61%, compared to 54% in the same period last year.
Operational Achievements:
Expansion of speciality services:
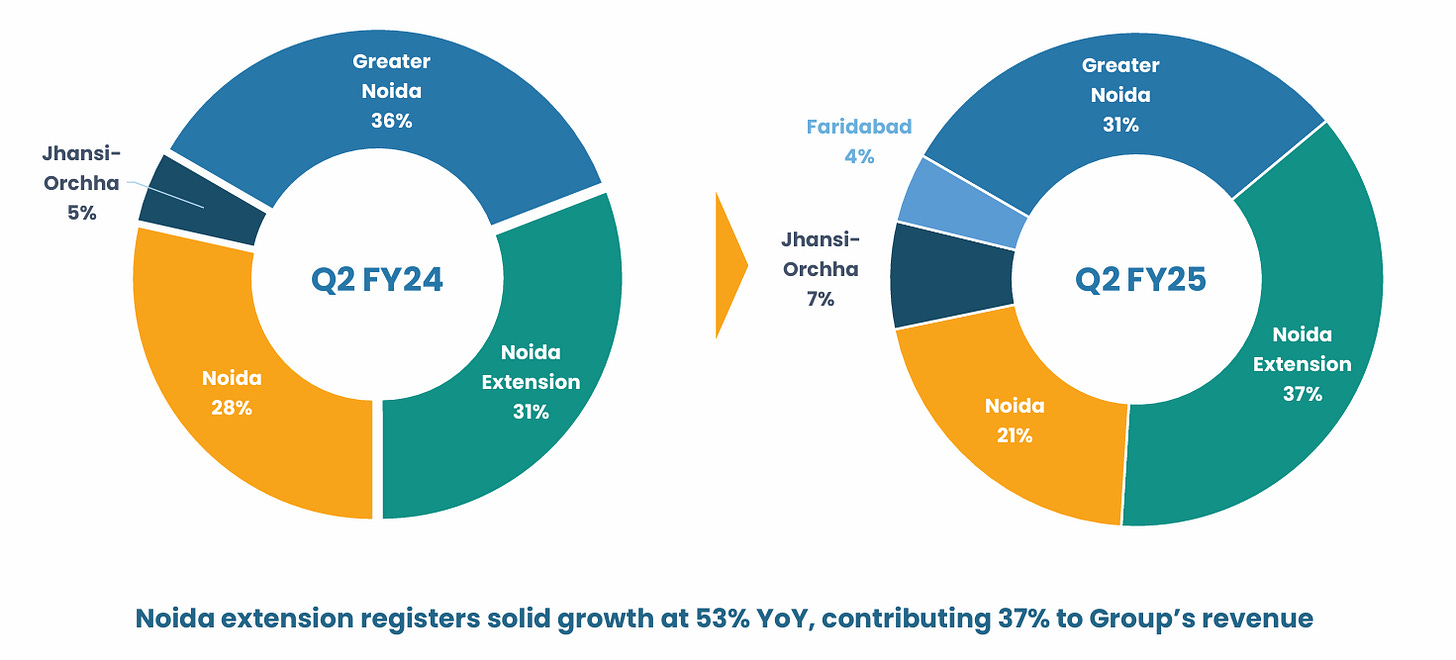
Oncology now contributes 20% of Noida Extension revenue and 11% of group revenue, marking a four-fold increase YoY.
Advanced technologies introduced, including PET scans and robotics.
Strategic acquisitions:
Acquired a 300+ bed hospital in Model Town, Delhi, for ₹160 crore, with an additional ₹60-70 crore planned for upgrades.
Acquired a majority stake in a 400-bed Faridabad hospital for ₹91 crore; the facility is expected to be operational by FY26.
Notable medical cases:
Successfully treated complex cases, including rare surgeries like open-heart excision of atrial myxoma and advanced gastroenterology procedures.
Quality and Recognition:
Noida Extension Hospital received JCI accreditation, the first hospital in Uttar Pradesh to achieve this on the first attempt.
13. SWOT ANALYSIS
Strengths:
Strong Revenue and Growth:
High ARPOB growth, particularly at Noida Extension, highlighting the increasing focus on high-value services like oncology and super-specialty care.
Strategic Acquisitions:
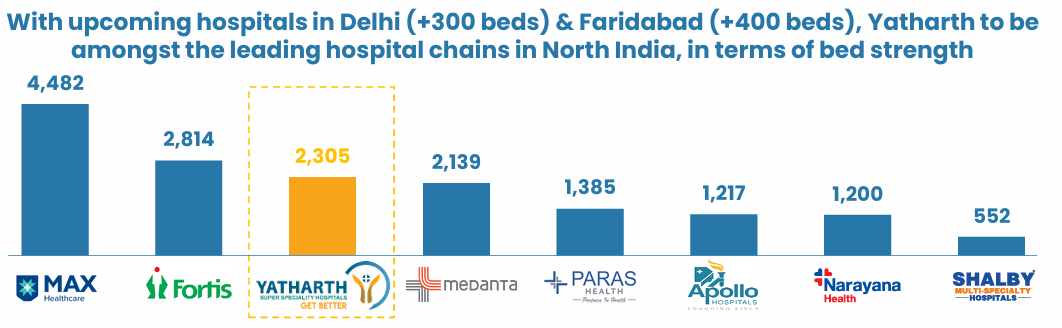
Recent acquisitions in key markets like Delhi and Faridabad enhance its regional presence and capacity, positioning the company as a major healthcare player in North India.
Industry Recognition:
The JCI accreditation for Noida Extension Hospital boosts brand credibility and trust, differentiating it from competitors.
Operational Excellence:
Successful implementation of advanced medical treatments and technologies such as PET scans and robotics, enhancing service offerings and patient outcomes.
Weaknesses:
EBITDA Margin Pressure:
The integration of new hospitals may temporarily reduce profitability, causing margin pressure as these facilities scale up.
Dependency on Doctor Costs:
Significant rise in doctor costs, driven by recruitment of high-profile doctors, which increases operational expenses.
Integration Challenges:
New acquisitions, while promising, may require significant investment in upgrading infrastructure, training staff, and acquiring new equipment, which could strain resources and slow down operational integration.
Opportunities:
Expansion into New Markets:
Model Town Delhi acquisition and plans to increase bed capacity to 300 beds are prime opportunities to capture the large urban healthcare market.
Growing Demand for Specialty Healthcare:
The growing trend for super-specialty healthcare services such as oncology, cardiology, and robotic surgeries offers a long-term revenue stream.
The ability to attract leading doctors to their facilities enhances service offerings and market positioning.
Government and Private Insurance Segment:
Shifting focus towards the private insurance and cash-paying segments, which are higher-margin compared to government business.
With government business set to reduce to 25%, this strategic shift can lead to improved profitability.
Technological Advancements:
Continued investment in cutting-edge medical technologies (e.g., radiation oncology, robotics) to drive growth in revenue, particularly in oncology services.
Threats:
Intense Competition:
Competition from large, established players such as Max Healthcare, especially in urban markets like Noida and Delhi, where other hospitals are also expanding their capacities.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks:
Healthcare regulations, insurance policies, and government reimbursements are subject to frequent changes, which could impact profitability, especially in the government business sector.
Economic Factors:
Rising costs of healthcare equipment and doctor fees could pressure margins, especially if the cost of high-end treatments cannot be fully passed on to patients.
Operational Risks in New Facilities:
The risk of underperformance in new facilities like the Faridabad and Delhi hospitals during the initial ramp-up phase.
14. Growth and Opportunity
Yatharth Hospital’s decision to plan a Qualified Institutional Placement (QIP) of ₹700 crores reflects its proactive approach to funding its growth strategy. The move aligns with the company’s ambitions to expand its hospital network and strengthen its position in the healthcare sector. Here's a detailed analysis:
i). Utilization of QIP Proceeds
- Acquisition Focus:
Approximately ₹400-450 crores of the QIP will be directed towards completing the recent acquisitions of hospitals in Model Town and Faridabad. These acquisitions are expected to add significant capacity to the company's operations and enhance its footprint in key growth markets.
ii). Leveraging Financial Strength
- Strong Cash Position:
With ₹250 crores of cash on the balance sheet, Yatharth is well-positioned to fund its immediate needs. This reserve offers flexibility for operational requirements or smaller capital expenditures.
- Debt Capacity:
The company has highlighted its ability to raise bank loans as required. By maintaining a healthy balance sheet and judiciously deploying cash, Yatharth ensures it has the financial bandwidth to seize future opportunities.
Key Growth Opportunity
The QIP-backed expansion positions Yatharth to capitalize on the growing demand for high-quality healthcare services in India. The funds will enable the company to:
I). Consolidate its presence in existing markets.
ii). Expand into untapped geographies with high potential.
iii). Explore value-accretive opportunities, such as high-ARPOB segments and premium offerings.
15. Growth Drivers for the company:
i). Expansion of Hospital Network
Faridabad and Delhi Hospitals: Addition of new hospitals in Model Town (Delhi) and Greater Faridabad to increase capacity and geographic reach.
700 Beds Addition by FY’26: Significant increase in operational capacity with strategic locations.
Strategic Locations: Proximity to high-demand areas like Noida Extension and Greater Noida, capitalizing on regional growth.
ii). Increasing ARPOB (Average Revenue Per Occupied Bed)
Focus on Super-Specialty Services: Expansion of high-margin services like liver transplants and bone marrow transplants, elevating ARPOB.
Faridabad Hospital as a Center of Excellence: Expected to achieve ARPOB levels similar to or higher than Noida Extension (₹38,000 ARPOB).
Optimized Payor Mix: Emphasis on cash and private insurance patients, with minimal government empanelment (20%-25% in new hospitals).
iii). Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Sustainability of Margins: Mature hospitals like Noida and Greater Noida achieveing margins of 28%-29% to offset initial drag from new hospitals.
Noida Extension Hospital: Significant occupancy ramp-up potential (currently ~60%) to drive higher margins.
Occupancy Leverage: Greater Noida’s growth is aligned with infrastructure developments like the upcoming airport.
iv). Diversified Patient Mix and Increased Footfall
Government Empanelments in Jhansi: Enhances patient volumes and accessibility.
Noida as a Healthcare Hub: Emerging competition (e.g., Max Hospital in Noida) fostering ecosystem growth, attracting patients who previously traveled to Delhi or Gurgaon.
Repeat Patients: Building patient loyalty through superior services.
v). Capitalizing on Evolving Market Trends
Noida and NCR Region Development: Growing healthcare needs as Noida evolves into a mature healthcare market, akin to Gurugram's transformation.
Healthcare Ecosystem Development: Increased availability of specialized doctors and services fostering overall market growth.
vi). Advanced Medical Services
Specialty Services Expansion: New service lines in transplants, advanced diagnostics, and tertiary care facilities, boosting revenues and attracting high-value cases.
Integrated Healthcare Model: Emphasis on creating centers of excellence for specific specialties to capture demand regionally and internationally.
16. Management Guidance
i). Revenue Growth
Industry-Leading Growth: The management expects revenue growth in FY'25 and FY'26 to surpass current year-on-year growth rates, driven by the addition of new hospitals and increasing patient volumes.
Contributions from New Hospitals: Newly acquired hospitals in Model Town (Delhi) and Greater Faridabad will begin contributing significantly to revenue after operational ramp-up.
ii). ARPOB Expansion
Initial ARPOB for New Hospitals: Faridabad Hospital is expected to match or exceed the ₹38,000 ARPOB achieved by the Noida Extension hospital, driven by super-specialty services like liver and bone marrow transplants.
Jhansi Hospital: ARPOB is expected to stabilize between ₹15,000-₹20,000 in the coming quarters as patient mix evolves and empanelments settle.
iii). Margin Sustainability
Group-Level Margins: EBITDA margins are guided to sustain at 25%-26%, despite potential drag from new hospitals. Mature hospitals like Noida and Greater Noida (with margins of 28%-29%) will help maintain consolidated margins.
Occupancy Ramp-Up: Occupancy improvement in Noida Extension (~60% currently) and Greater Noida hospitals will support margin growth.
iv). Operational Focus
Payor Mix Strategy: For new hospitals, the management intends to limit government business to 20%-25%, focusing on private insurance and cash-paying patients to ensure higher margins.
Empanelments: Empanelment of private and government insurance for newly operational hospitals will be completed over the next few months.
Key Targets
ARPOB Growth: Maintain and grow ARPOB across all hospitals.
Revenue Growth: Outpace industry averages with consistent year-on-year growth.
EBITDA Margins: Sustain margins at 25%-26%, leveraging mature hospital performance to offset new hospital drag.
17. Competitors in the Market:
1. Apollo Hospitals – Leading hospital chain with strong diagnostics and pharmacy services.
2. Sun Pharma – Largest pharmaceutical company, focusing on generics and specialty medicines.
3. Fortis Healthcare – Major hospital network excelling in specialized care and medical tourism.
4. Dr. Reddy’s Labs – Pharma giant with a global presence in generics and biosimilars.
5. Narayana Health – Affordable healthcare pioneer with a focus on cardiac and rural markets.
Competitive Advantages and Strategic Insights
I). Entry Barriers: High capex, regulatory hurdles, and specialized offerings protect against new entrants.
ii). Pricing Power: The ability to raise ARPOB ensures margin protection despite rising costs.
iii). Sector Leadership Potential: Although not yet the largest, consistent growth and high margins position Yatharth for leadership in select geographies.
Final Thought
A robust business model, like Yatharth’s, prioritizes long-term scalability and operational strength. While the balance sheet may fluctuate due to capex cycles, its competitive advantages and enduring strategies ensure sustainability and potential for high P/E ratings in the future. This aligns with the principle that a strong business model can repair a balance sheet, but not vice versa.
18. Industry Overview:
Introduction:
India's healthcare sector is a major revenue and employment driver, spanning hospitals, medical devices, telemedicine, medical tourism, and insurance. It benefits from public and private systems, with the private sector dominating advanced care. India's strengths include a skilled medical workforce and cost-competitive services, with surgery costs one-tenth of Western rates. This has boosted medical tourism and R&D, making India a global healthcare hub.
Market size:
The Indian healthcare industry grew to $372 billion in 2023, employing 7.5 million people, with tech advancements expected to add 2.7–3.5 million jobs. Public healthcare spending rose to 2.1% of GDP in FY23, while the hospital market is projected to double to $193.59 billion by 2032.
Source - IBEF
Trends:
Telemedicine: Major hospitals have adopted telemedicine services and entered into a number of PPPs.
Artificial intelligence: AI for keeping health records & providing best possible treatment to patients at the right time
Mobile & Wearable Devices: India is emerging as a strong market for wearables, with approximately 2 Mn units sold in 2017, expected to reach 129 Mn units in 2030.
Robotic Surgeries: India's surgical robotics market is estimated to expand at a CAGR of 20% (2017-25) to hit the size of $350 Mn by 2025.
Source - invest india
Growth Driver's:
Robotic process automation (RPA): RPA to improve the efficiency of the healthcare workforce; reducing costs and creating the value proposition
Shifting Disease Burden: Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) account for 50% of the disease burden and 60% of all deaths in India
Policy Support & Incentives: 100% FDI allowed in Greenfield & Brownfield projects, measures to correct unfavourable duty structure are being undertaken, single window clearance e-portal to improve EoDB
Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan - Self Reliant India: A special economic and comprehensive package of INR 20 lakh Cr towards promoting manufacturing in India.
Insurance Coverage: 20% Indians covered; expected to rise with rising incomes, urbanization
Emergence of telemedicine: Along with these, the emergence of telemedicine, and government initiatives like e-health married with tax benefits and incentives are driving the healthcare market in India.
Medical Infrastructure: Over $200 Bn to be spent on medical infrastructure by 2024.
Source - invest india
Challenges:
The healthcare industry in India faces many challenges, including:
Inadequate infrastructure: There are not enough healthcare facilities, especially in rural areas. The government has mandated that private medical colleges be built on at least five acres of land, which has led to them being built in rural areas.
Shortage of healthcare professionals: There is a shortage of doctors, nurses, and paramedical staff. Burnout is a major factor in this shortage, due to increased workloads during the pandemic and the growing number of administrative tasks.
Urban-rural disparities: There is a significant difference in the quality and accessibility of healthcare services between urban and rural areas.
Financial constraints and health insurance: Many Indians face high out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare services. Insurance only covers about a fifth of the population.
Preventive care: Preventive care is undervalued in India, despite its benefits.
Lack of medical research: India receives little attention for R&D and new projects led by cutting-edge technology.
Future Prospects:
The healthcare industry in India is poised for significant growth and transformation in the coming years. Several factors are driving this growth:
1. Increasing Demand:
Aging Population: India's aging population will lead to increased demand for healthcare services, particularly geriatric care.
Rising Income Levels: As disposable incomes rise, more people will invest in preventative healthcare and advanced medical treatments.
Growing Awareness: Increased awareness about health and wellness is driving demand for preventive care and early diagnosis.
2. Government Initiatives:
Ayushman Bharat: This government-sponsored health insurance scheme provides affordable healthcare to millions of Indians, boosting demand for healthcare services.
Digital Health Initiatives: The government's focus on digital health, including telemedicine and electronic health records, is improving access to healthcare in remote areas.
3. Technological Advancements:
Telemedicine: Remote consultations and monitoring are becoming more prevalent, especially in rural areas.
4. Medical Tourism:
India's affordable healthcare costs and skilled medical professionals are attracting medical tourists from around the world.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry:
India is a major global pharmaceutical hub, producing generic drugs and vaccines at affordable prices.
Thank you for reading till the end! We hope you enjoyed this report.
Researched By- Naresh, Mayank and Vaibhav
All information is sourced from company annual reports, Screener.in, industry reports and Economy Outlook reports.
Disclaimer- We do not recommend buying or selling any stock. You should consult your financial advisor before buying or selling any financial instrument.
Thanks for reading EquityEdge Research! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support our work.



































For QIB, the price at which shares are issued may also be mentioned for complete info...thanks