Introduction:
HDFC Bank, India’s largest private sector bank by market capitalization, stands as a testament to resilience and adaptability in the ever-evolving banking industry.
The bank has changed drastically in the last year, putting it in a better position to handle the complicated financial environment.
From completing a historic merger to implementing groundbreaking technological upgrades, HDFC Bank has taken bold steps to maintain its leadership position and adapt to growing customer demands.
In this piece, we'll explore the significant turning points, difficulties, and chances that have shaped HDFC Bank's recent history and consider how it has influenced the direction of Indian banking.
The Landmark Merger with HDFC Ltd: Building a Financial Behemoth
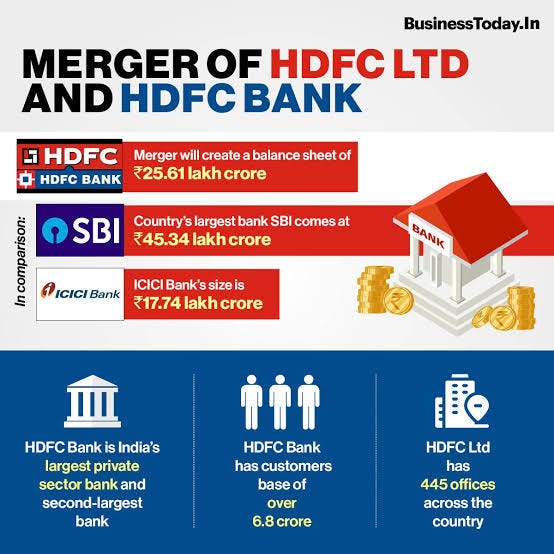
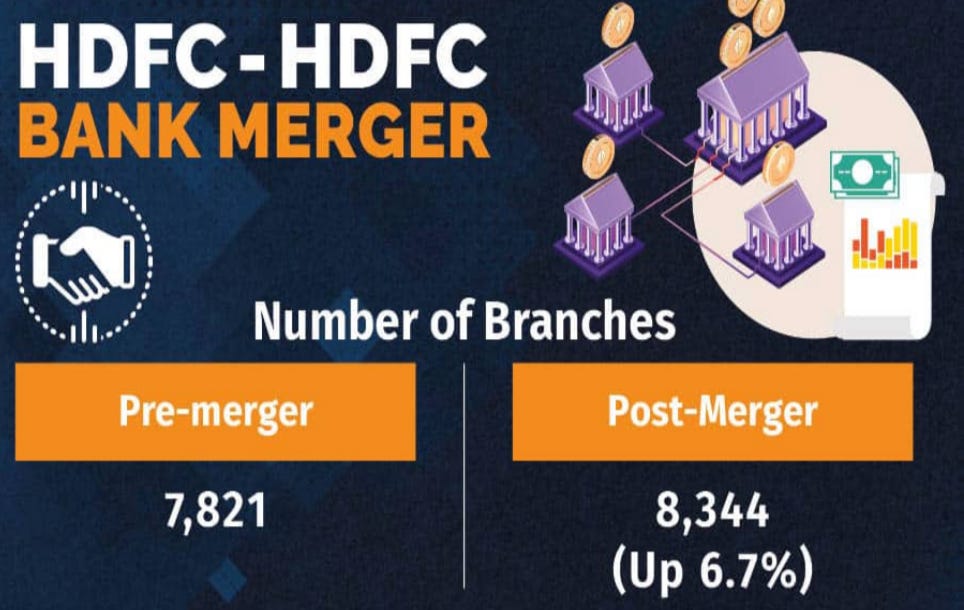
In July 2023, HDFC Bank finalized its merger with Housing Development Finance Corporation (HDFC Ltd), marking one of the largest mergers in the history of India’s financial sector.
The combined entity has created a financial powerhouse with assets exceeding ₹25 lakh crore and a customer base of more than 120 million individuals.
This merger has had far-reaching implications for both the bank and the broader Indian financial ecosystem.
Prior to the merger, HDFC Ltd was the country’s largest housing finance company, providing long-term home loans.
By integrating its expertise in housing finance with HDFC Bank’s extensive banking infrastructure, the merger has unlocked significant synergies.
HDFC Bank is now better positioned to cross-sell products to a broader customer base, leveraging the housing finance expertise of HDFC Ltd while offering a comprehensive suite of financial services.
For instance, a home loan customer can now seamlessly access credit cards, personal loans, and investment services, creating a one-stop solution for financial needs.
However, while the merger opens doors to immense growth, it has also brought new challenges, particularly in managing the bank’s financial ratios and operational complexity.
Post-Merger Adjustments: Addressing Financial and Operational
One of the most notable shifts post-merger has been the bank’s loan-to-deposit ratio (LDR). Historically, HDFC Bank maintained an LDR of around 86-87%, reflecting a balanced approach to lending and deposit mobilization.
However, with the merger, the ratio surged to approximately 110%.
The increase in LDR indicates that the bank is lending significantly more than its deposits, which, while fueling growth, also poses liquidity risks.
To mitigate this, HDFC Bank has outlined a strategic roadmap to reduce the LDR to pre-merger levels within two to three years.
(Source - Reuters)
The Strategy includes:
1. Moderating Loan Growth: While the bank remains committed to expanding its lending portfolio, it plans to slow down growth in high-risk segments temporarily.
2. Deposit Mobilization: The bank has launched aggressive campaigns to attract more deposits, offering competitive interest rates and expanding its reach into rural and semi-urban markets.
Moreover, the operational integration of HDFC Ltd’s employees, systems, and processes into HDFC Bank has been a massive undertaking.
Aligning the cultures and operational frameworks of two large organizations requires meticulous planning and execution, especially when customer experience and trust are at stake.
Changes after the Merger:
Technological Transformation: Core Banking System Upgrade
As HDFC Bank continues to expand its footprint, One cannot stress the value of having a strong technology foundation. As a result, the bank is switching to a new designed platform for its Core Banking System.
This migration is expected to bring multiple benefits, including:
Enhanced Speed: Transactions and processes will be executed faster, improving the overall customer experience.
Scalability: The new system can handle a significantly larger number of transactions, catering to the bank’s growing customer base.
Reliability: Upgrading to a modern platform reduces the likelihood of system outages, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery.
In addition to core banking upgrades, HDFC Bank has also invested heavily in digital transformation initiatives.
Its mobile banking app and internet banking platforms now offer enhanced features, such as AI-powered financial advice, personalized product recommendations, and seamless integration with third-party services.
This focus on technology underscores HDFC Bank’s commitment to staying ahead of the curve in a banking industry increasingly driven by digital innovation.
Regulatory Recognition: A 'Too Big to Fail' Institution
HDFC Bank’s importance to the Indian financial system was reaffirmed when the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) included it in its list of Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) in November 2024.
Often referred to as “too big to fail,” this designation recognizes banks whose failure could have a significant impact on the economy.
As a D-SIB, HDFC Bank is required to maintain additional regulatory capital buffers. Effective April 2025, it will need to hold an additional 0.40% of its risk-weighted assets as capital. While this increases the bank’s compliance requirements, it also reassures customers and investors about the bank’s financial stability.
Being a D-SIB also underscores the bank’s pivotal role in driving economic growth, as it continues to support infrastructure projects, housing development, and retail credit.
(Source - Reuters)
Stock Market Performance: Reflecting Investor Sentiment
HDFC Bank’s stock performance in 2024 has mirrored its ongoing transformation. On December 24, 2024, the stock closed at ₹1,797.65, slightly below its 52-week high of ₹1,880.00. While the price remains strong, recent trading volumes have been lower than the 50-day average, indicating a cautious sentiment among investors.
This caution could be attributed to several factors, including:
The ongoing financial adjustments post-merger.
Concerns over the rising loan-to-deposit ratio.
Macroeconomic challenges, such as inflation and global economic uncertainty.
However, analysts remain optimistic about the bank’s long-term prospects. The merger with HDFC Ltd is expected to unlock significant value over time, and the bank’s focus on technology and regulatory compliance positions it well for sustainable growth.
Expanding Customer Reach: Rural and Semi-Urban
A key pillar of HDFC Bank’s growth strategy is its focus on expanding into rural and semi-urban markets. These regions remain underserved by traditional banking services, presenting a massive opportunity for growth.
Post-merger, the bank has ramped up efforts to penetrate these markets by:
Opening new branches and ATMs.
Partnering with fintech companies to offer digital banking solutions tailored to rural customers.
Providing financial literacy programs to educate customers about the benefits of banking services.
This approach aligns with the government’s broader vision of financial inclusion and positions HDFC Bank as a key enabler of economic development in these regions.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
1. Integrating Operations Post-Merger: Achieving seamless integration while maintaining service quality.
2. Managing Financial Ratios: Balancing growth with liquidity and regulatory compliance.
3. Adapting to Competition: Competing with fintech startups and other private sector banks in the digital space.
Opportunities
1. Unlocking Synergies: Leveraging the strengths of HDFC Ltd to cross-sell products and increase revenue.
2. Expanding Market Share: Penetrating underserved markets with innovative products.
3. Strengthening Digital Presence: Using technology to enhance customer experience and reduce cost.
Conclusion: A Cornerstone of India’s Financial System
HDFC Bank’s journey over the past year has been nothing short of transformative. The merger with HDFC Ltd has created a financial powerhouse, while its technological upgrades and regulatory compliance efforts demonstrate its commitment to operational excellence.
While challenges remain, HDFC Bank’s strategic initiatives position it well to maintain its leadership in the Indian banking sector. As the bank adapts to a changing landscape, it continues to set benchmarks for innovation, customer service, and financial stability.
With a robust foundation and a clear vision for the future, HDFC Bank remains a cornerstone of India’s financial system, playing a pivotal role in driving economic growth and development.
If you like the hard work we put in, you can invest in us:
For our Non-Indian audience: You can donate to us through PayPal. Click here.
For our Indian audience, UPI QRs are given below: